
文章目录
WHAT IS THE BEST 3D SCANNER?
3D scanners are less popular than 3D printers, but they are an important part of the 3D printing ecosystem. Many different types of 3D scanners exist, from desktop 3D scanners to handheld 3D scanners and advanced metrology systems.
3D scanners can be used for an extremely wide range of applications, from reverse engineering to 3D body scanning or even online retail. They are becoming much easier to use and are available at much lower prices than ever before.
However, given the low number of reliable 3D scanner reviews, it can be challenging to find the best 3D scanner.
TOP 10 3D SCANNERS IN 2020
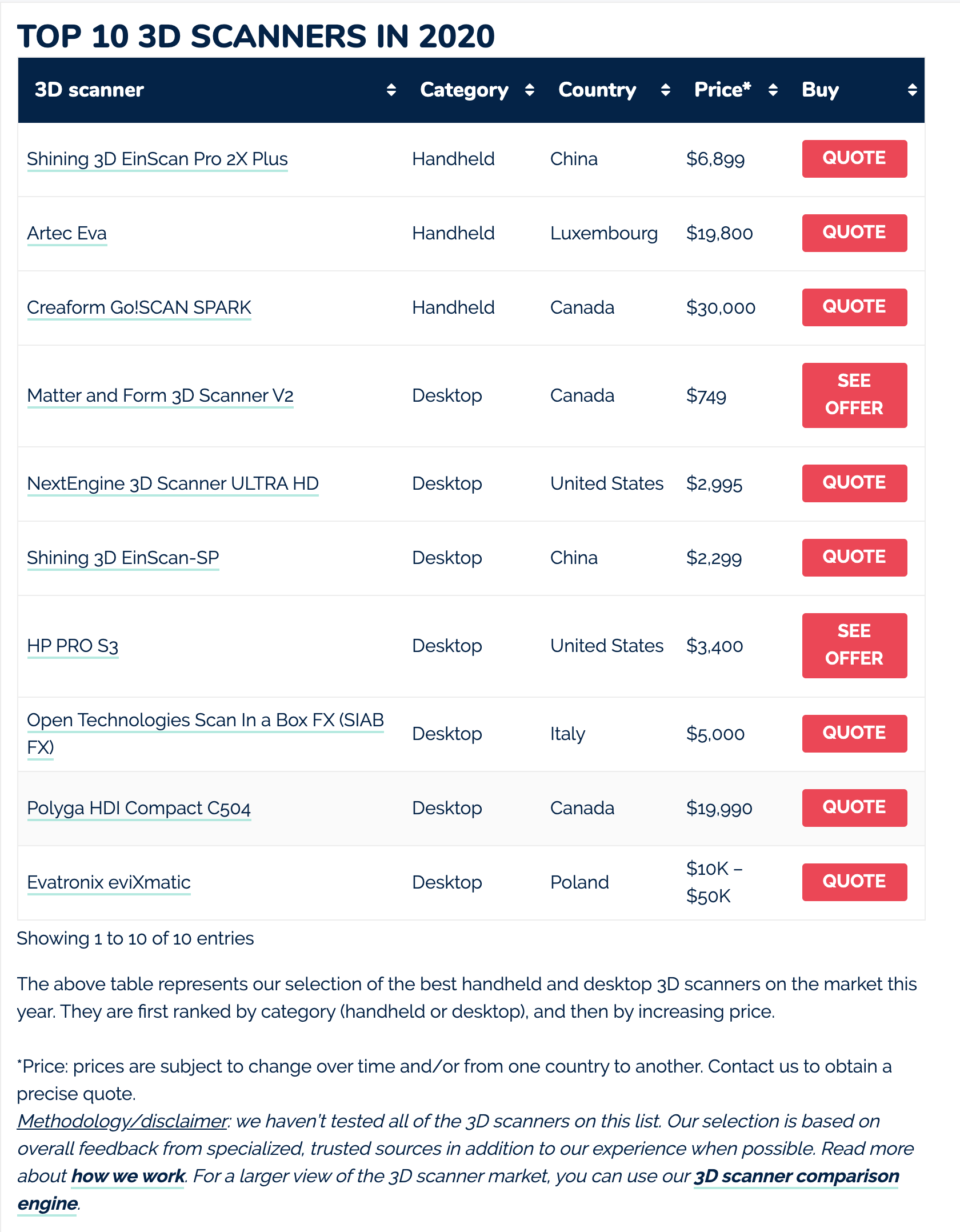
3D scanner recommendations
Desktop 3D scanners
Desktop 3D scanners can be ideal for both professionals and hobbyists that need to scan small parts. They tend to be more accurate since you aren’t holding and moving the 3D scanner around yourself.
Also, many desktop 3D scanners come with (or at least optionally) an automatic turntable, which makes it much easier to get clean 3D scans.

Handheld 3D scanners
Handheld 3D scanners, sometimes called portable 3D scanners, can be used to 3D scan small to very large objects. These 3D scanners can also be used to reach hard-to-reach places. The precision and the ability to capture color and texture will depend on the 3D scanner model.

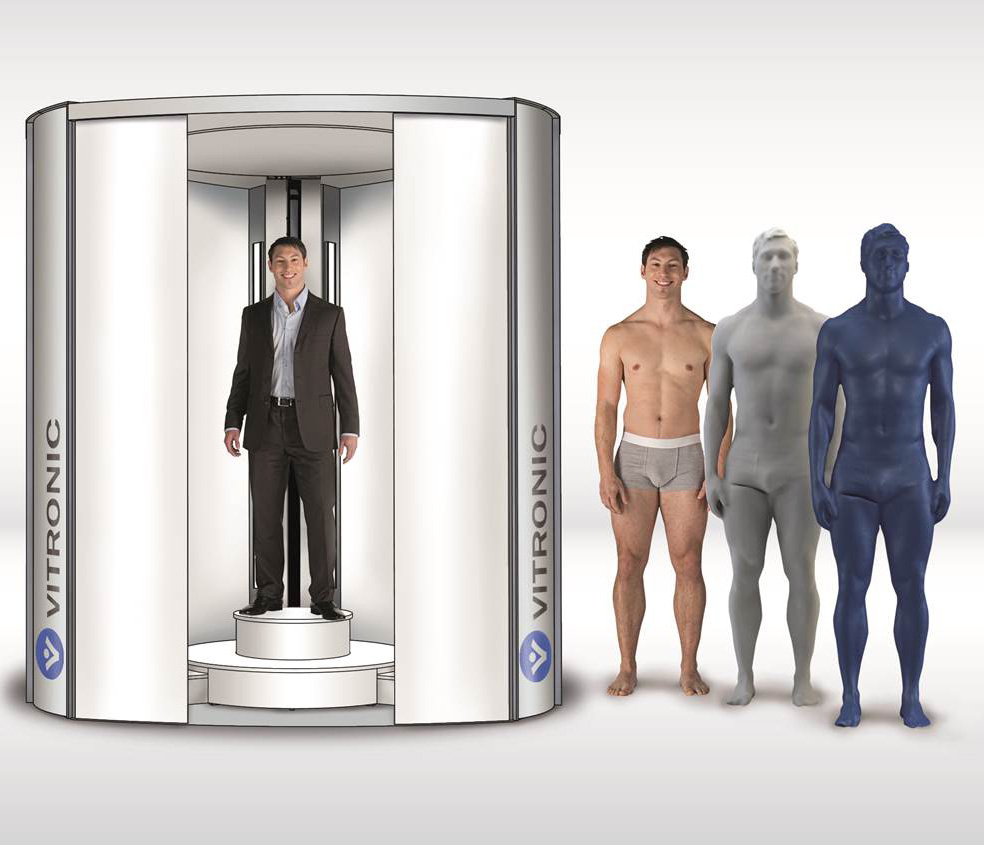
3D body scanners
3D body scanners can be used in very various fields.
- Professionals: professionals might want to 3D scan a person to make a 3D figurine, prepare for a surgical intervention, follow-up on a pregnancy or skin conditions, etc.
Individuals: 3D body scanners can be used to help with fitness goals and personal shape. These 3D scanners usually can’t capture color and texture but offer a high resolution.

##3D scanning mobile apps
3D scanning mobile apps are designed for occasional users that are not willing to or are unable to invest in a 3D scanner. They are not as precise as most 3D scanners, but mobile apps are a great way to get initiated to 3D scanning. Check out our list of the best 3D scanning apps for more information.
3D SCANNING APPLICATIONS
There are many reasons to buy a 3D scanner, for various industries and applications.
Jewelry
Jewelers are starting to use 3D printing and 3D scanning to build casts in order to create amazing jewels. Read more on our 3D printing and 3D scanning for jewelry page.
Dental
Dentists and dental labs are using 3D printing to build and create various dental appliances. Find more information on our 3D printing and 3D scanning for the dental industry.
Medical
3D scanners are very versatile and can be used in many different ways in healthcare, from studies to making prosthetics or studying a person’s posture. Find more information on our 3D scanning and 3D printing for the medical industry page.
3D figurines and 3D selfies
3D portraits or mini-me are increasingly popular! To make one, you get 3D scanned, and you can print your mini lookalike. To learn more about the subject, you can visit our 3D printed figurines, 3D selfies and 3D portraits page.
Architecture
Architects can use 3D scanning to capture an area, building or habitation and present it in a more efficient way to their clients. If you are interested, you’ll find more information on our 3D scanning and 3D printing for architects page.
Archeology and museums
Archaeologists, museum curators and researchers are starting to use 3D scanning to get a better view and capture ancient pieces. To read more about this topic, you can visit our 3D printing and 3D scanning in archeology and cultural preservation page.
Reverse engineering
Reverse engineering, also known as back engineering, is the process of extracting information of anything man-made and studying it. 3D scanners can be used to capture all the parts of a disassembled object to create a 3D model. The user will then be able to digitally study it in 3D afterwards.
Metrology/inspection
Industries need to make sure their factories are producing perfect products that are perfectly in line with the products’ reference dimensions. 3D scanners can be used to efficiently measure potential discrepancies.
OVERVIEW OF 3D SCANNING TECHNOLOGIES
Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry consists of taking measurements from photographs to recover the exact positions of surface points.
The principle of photogrammetry is to analyze several photographs of a static subject, taken from different viewpoints, and to automatically detect pixels corresponding to a same physical point.
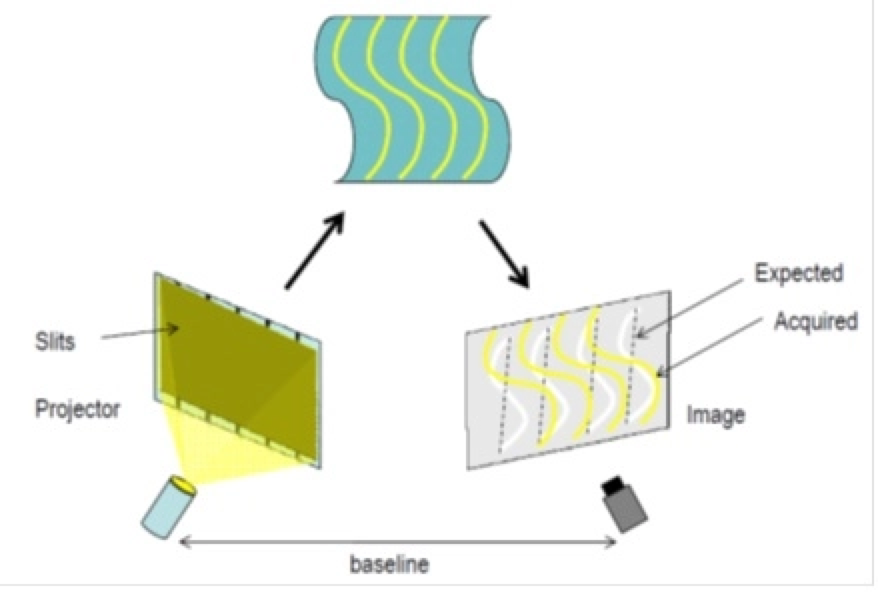
Structured light
3D scanners using structured light projects a series of linear light patterns onto an object.
The system is then able to examine the deformations of each line and to calculate the distance between the 3D scanner and the object’s surface. With this data, the software is able to build an accurate 3D model of the object.
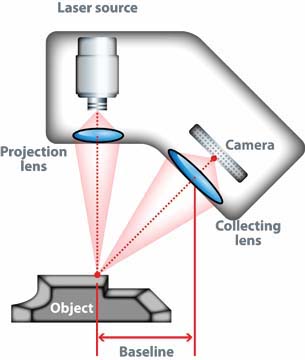
Triangulation
A 3D scanner using triangulation technology will project a laser beam on the object’s surface and measure the deformation of the laser ray (similar to structured light, but with one or more lasers).
Contact
Contact 3D scanners probe the subject via physical touch. While the object is firmly held in place, a touch probe moves along its surface to record 3D information.
For more precise and detailed explanations, you can visit our 3D scanning technologies page.